Anatomy & Physiology Lesson
| HOME | Biology | Anatomy | Yearbook | Links |
The Heart
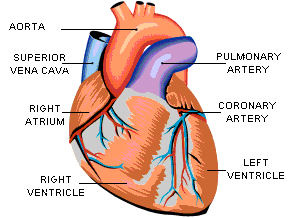
The Function of the Heart The heart is a muscle about the size of your fist. It acts as a pump that contracts and pushes blood through the vessels of the body to deliver oxygen and nutrients to cells. The average adult heart beats approximately 100,000 times each day or 38 million times each year. The Flow of Blood The heart is divided into two pumping systems. The right side of the heart receives the deoxygenated blood and pushes it to the lungs to replenish its oxygen supply. The left side of the heart receives the newly oxygenated blood from the lungs and pushes it to all of the vessels in the body to supply the cells.
Chambers of the Heart The heart is made up of four chambers: the right atrium, the left atrium, the right ventricle, and the left ventricle. The atria are designed as holding tanks to receive the blood and then drain it into the ventricles. The ventricles are the pumping chambers. They contract and push the blood out of the heart. Valves of the Heart There are four valves found in the heart to help prevent blood backflow. There are two atrioventricular valves called the bicuspid and tricuspid valves. These valves separate the atria and ventricles. The atrioventricular valves open when the heart is relaxed to allow blood to drain into the ventricles. But, when the heart contracts they are forced shut so that blood does not move back into the atria. The other two valves are found at the base of the aorta (the large vessel that leaves the heart and branches to all of the vessels in the body) and the base of the pulmonary trunk (the large vessel that leaves the heart and branches into the vessels of the lungs). These valves are designed to prevent blood from flowing back into the ventricles when the heart relaxes. So, these valves are forced open with the heart contracts and then slam shut when the heart relaxes.
|
Interactive Activities & Animations
Helpful Links
|
|---|
Copyright 2007, Amanda Smith. All Rights Reserved